Daniel Kowal, MD, RMSK | Radquarters
@Radquarters
Radiologist & teacher: Body imaging, ultrasound, MSK radiology & more. Watch 📽️ Lectures: https://t.co/RrUYKt4dVP
ID:1094564487800197120
https://radquarters.com/ 10-02-2019 11:51:24
327 Tweets
5,8K Followers
372 Following


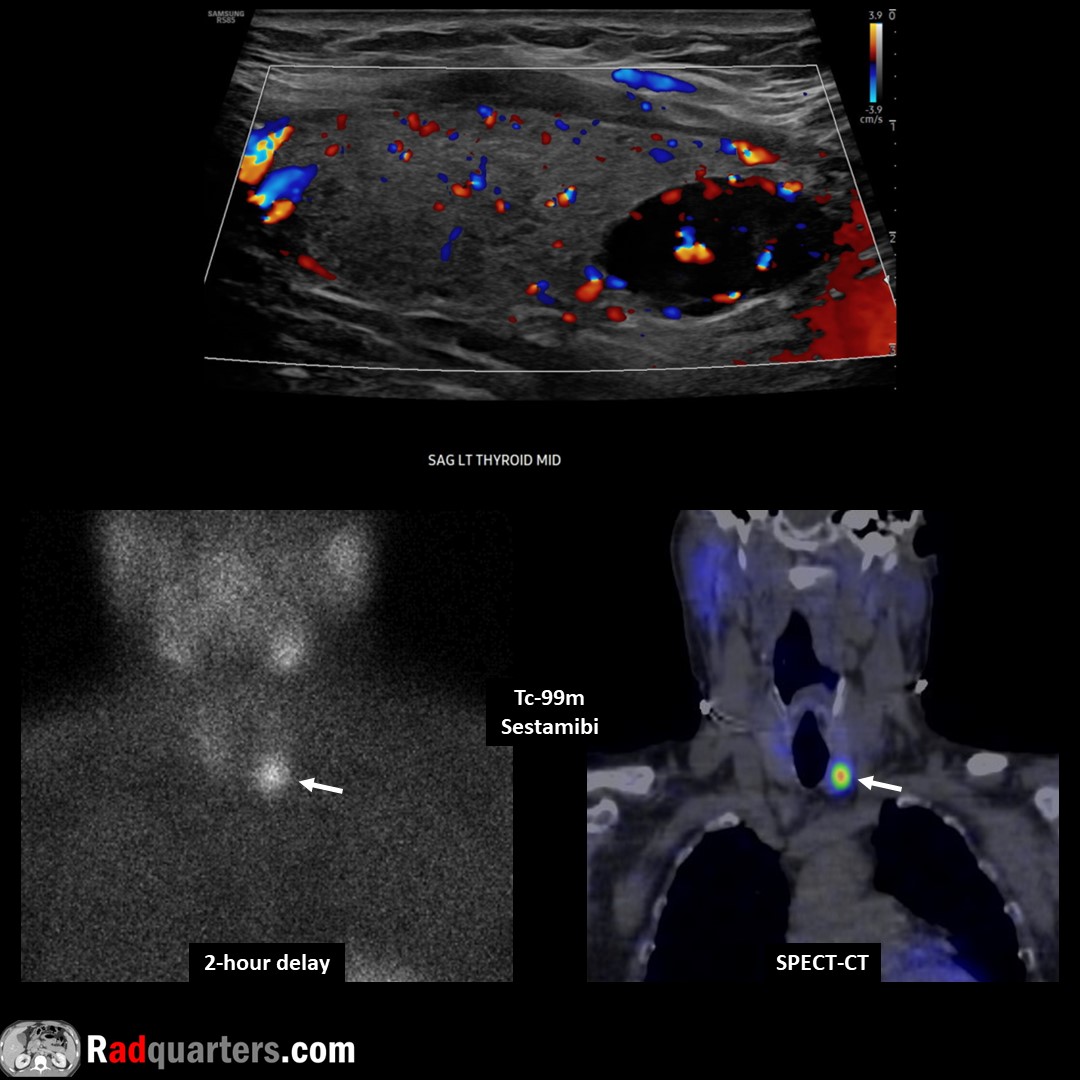
Large parathyroid adenoma. Usually oval/bean-shaped, but larger adenomas can be multilobulated. “Polar vessel” sign = Enlarged feeding artery or draining vein terminating @ parathyroid adenoma. Watch📽️ to learn more: bit.ly/pt-adenoma
Boston Imaging Samsung Healthcare #FOAMrad


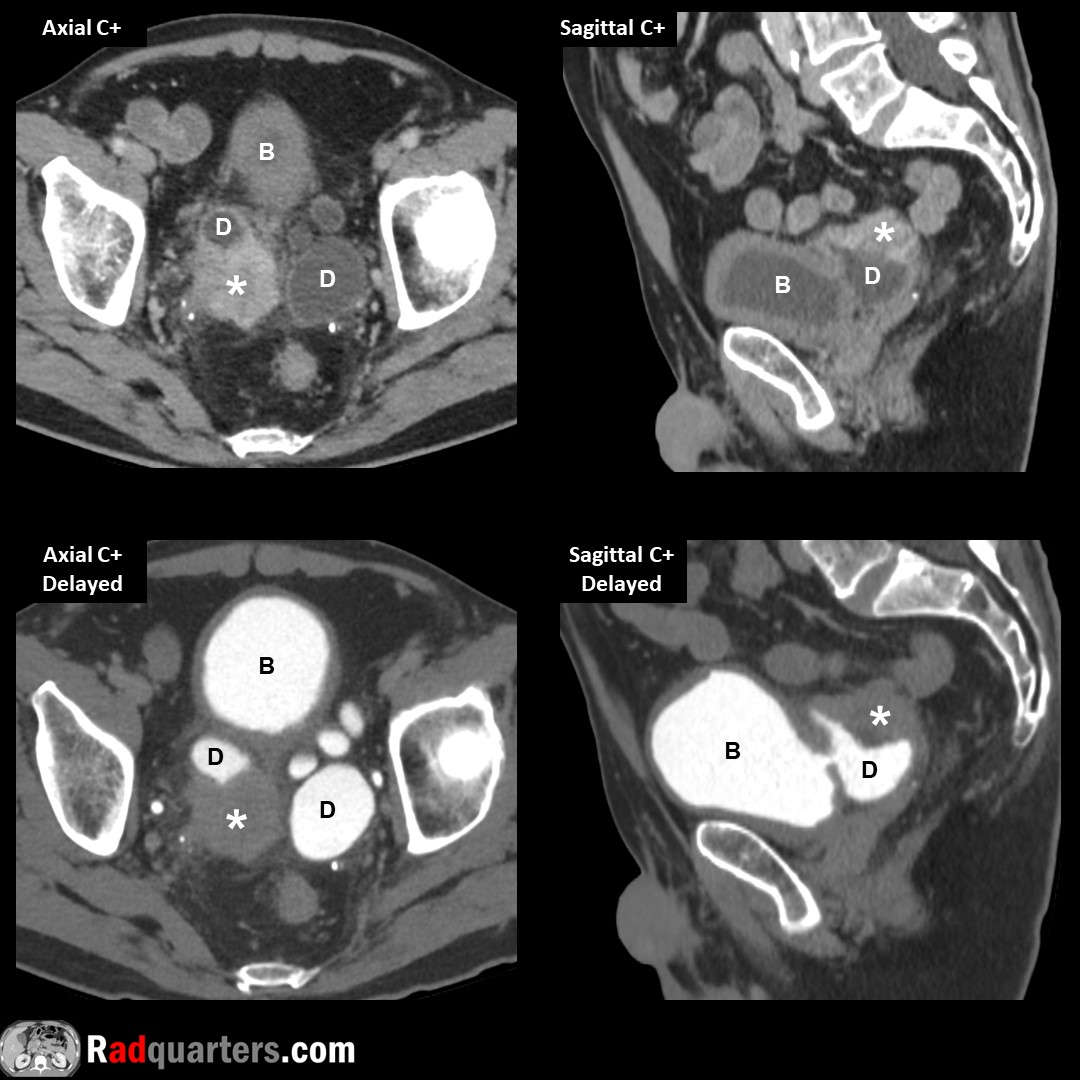
Parathyroid adenoma. Tc-99m sestamibi: Radiotracer initially taken up by both thyroid & parathyroid tissue but washes out more rapidly from thyroid & persists in adenoma on delayed images. Watch📽️ to learn more: bit.ly/pt-adenoma
Boston Imaging Samsung Healthcare #FOAMrad

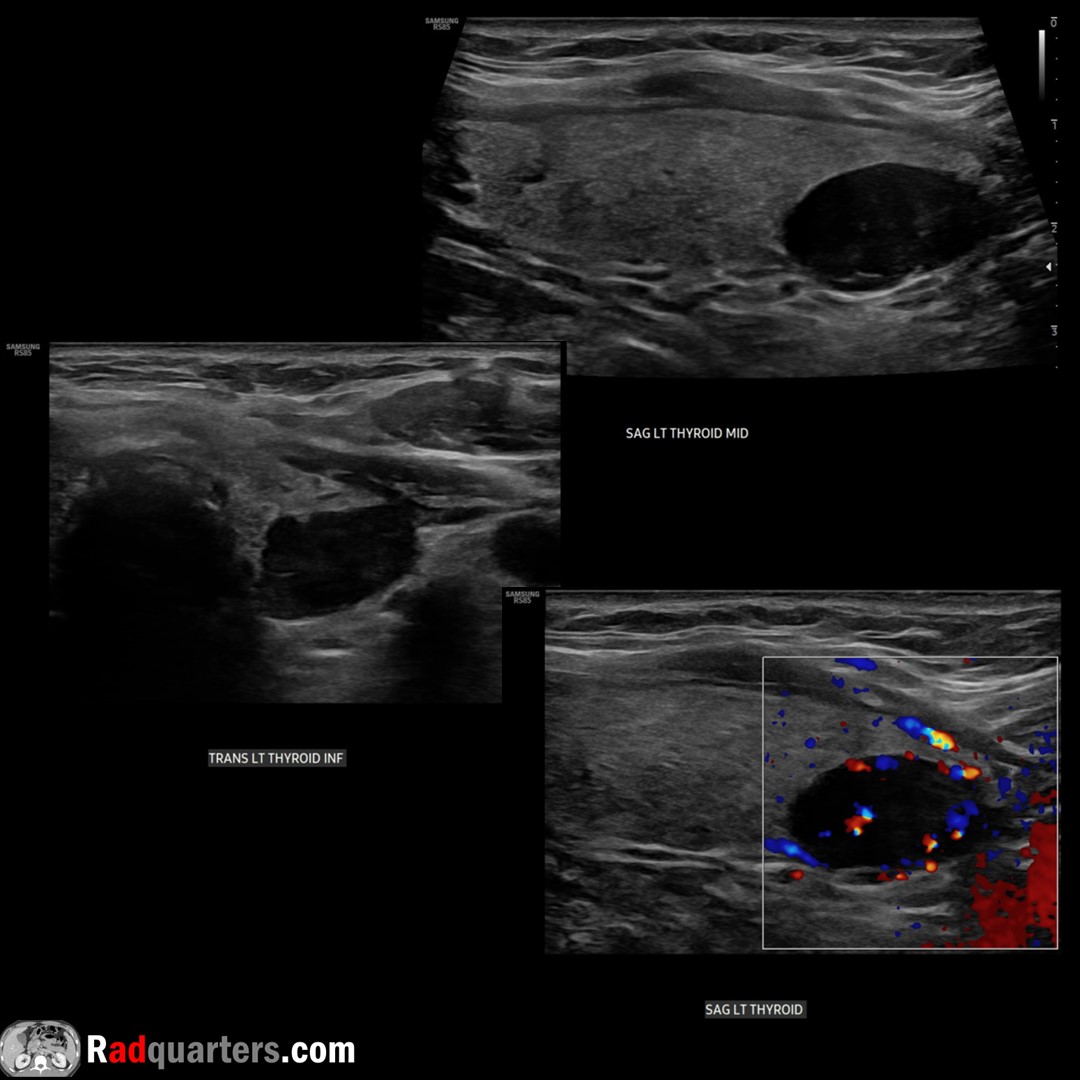
Parathyroid adenoma. Most common cause of primary hyperPTH. Solid, homogeneous & very hypoechoic. Oval/bean-shaped, long axis craniocaudal. Hypervascular. Bright line separates from thyroid. Watch📽️ to learn more: bit.ly/pt-adenoma
Boston Imaging Samsung Healthcare #FOAMrad



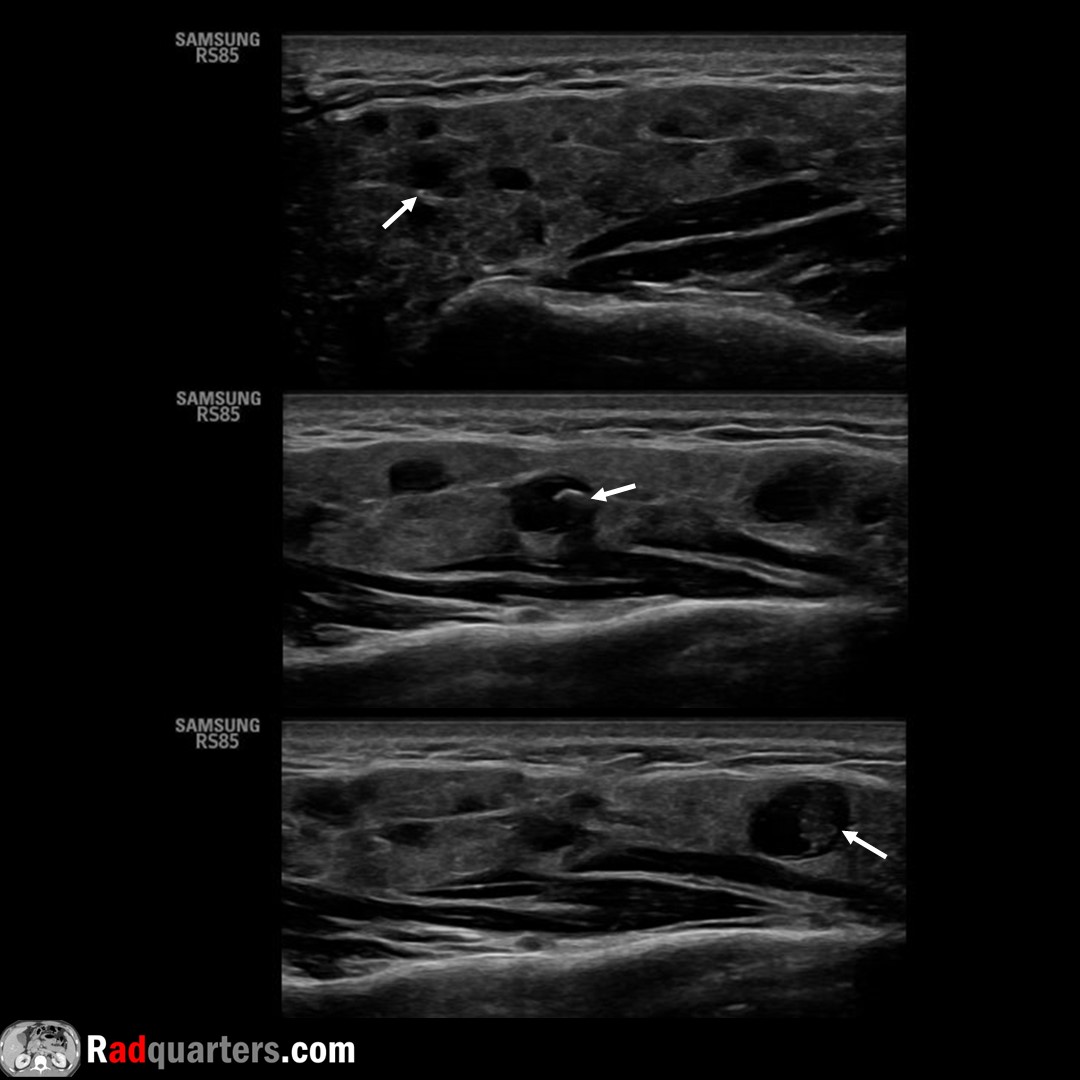
Juvenile recurrent parotitis. Multiple nonuniform hypoechoic foci scattered throughout gland with central calcifications (arrows). Rare but 2nd most common cause of parotitis in childhood after mumps. Watch📽️ to learn more: bit.ly/rq-parotitis
Boston Imaging Samsung Healthcare

Pomegranate sign of acute parotitis. Uniform anechoic foci scattered throughout the gland. Similar to pseudonodular “giraffe” ultrasound pattern that can be seen in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Watch📽️ to learn more: bit.ly/rq-parotitis
Boston Imaging Samsung Healthcare #FOAMrad
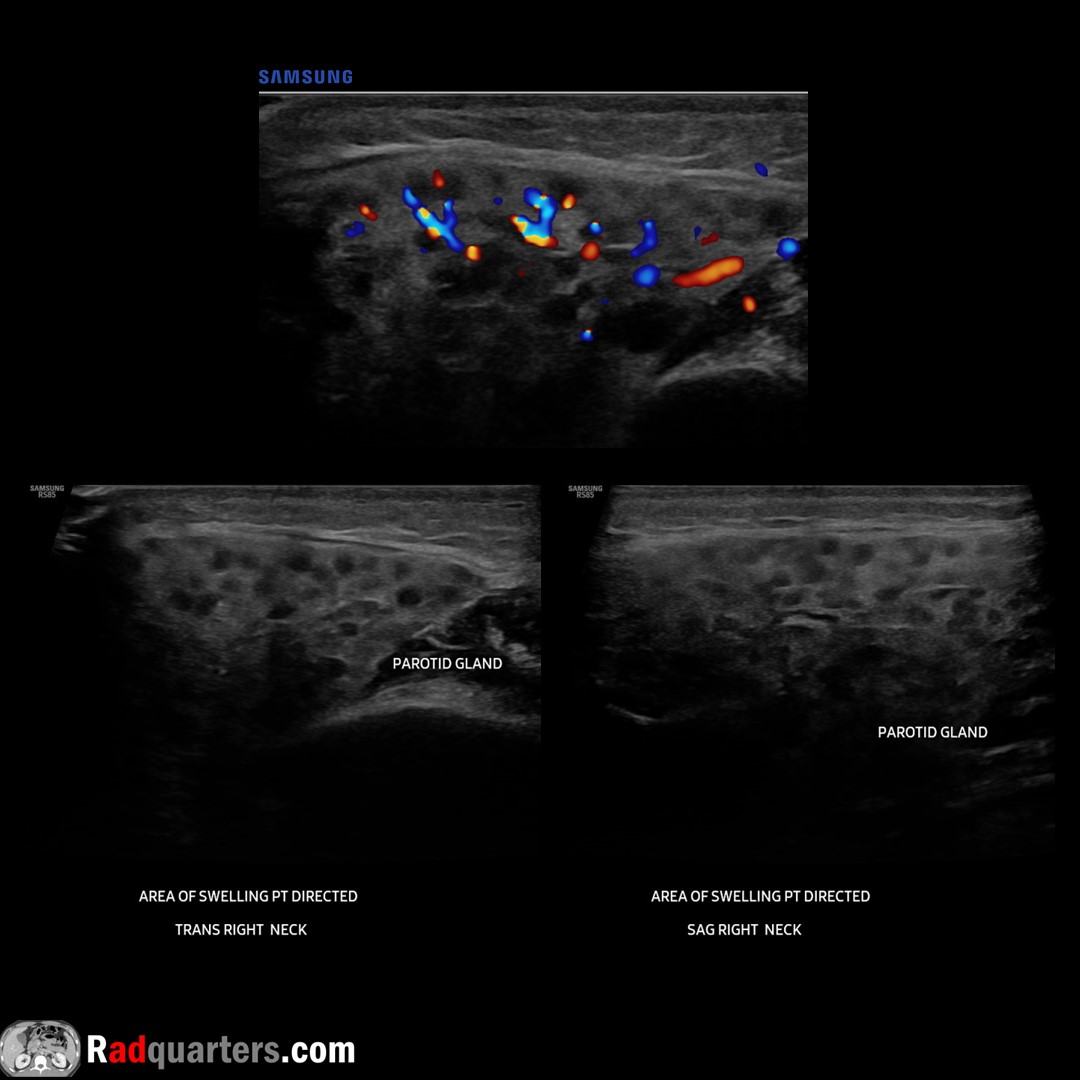

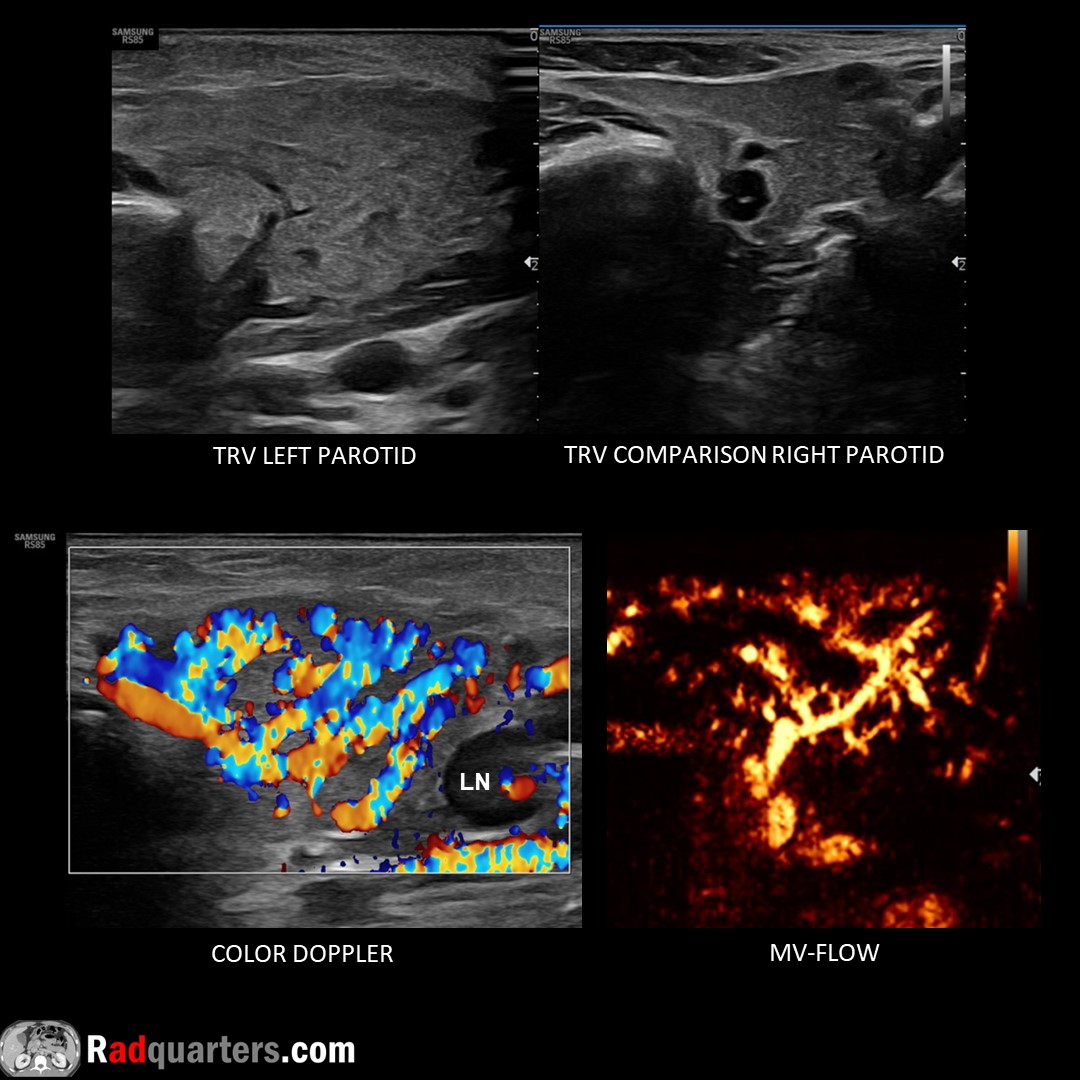
Acute left parotitis. 2 y.o. with enlarged, heterogeneous, hyperemic left parotid gland with adjacent lymphadenopathy (LN). Normal right gland. In children, most common cause viral (mumps). Watch📽️ to learn more: bit.ly/rq-parotitis
Boston Imaging Samsung Healthcare #FOAMrad

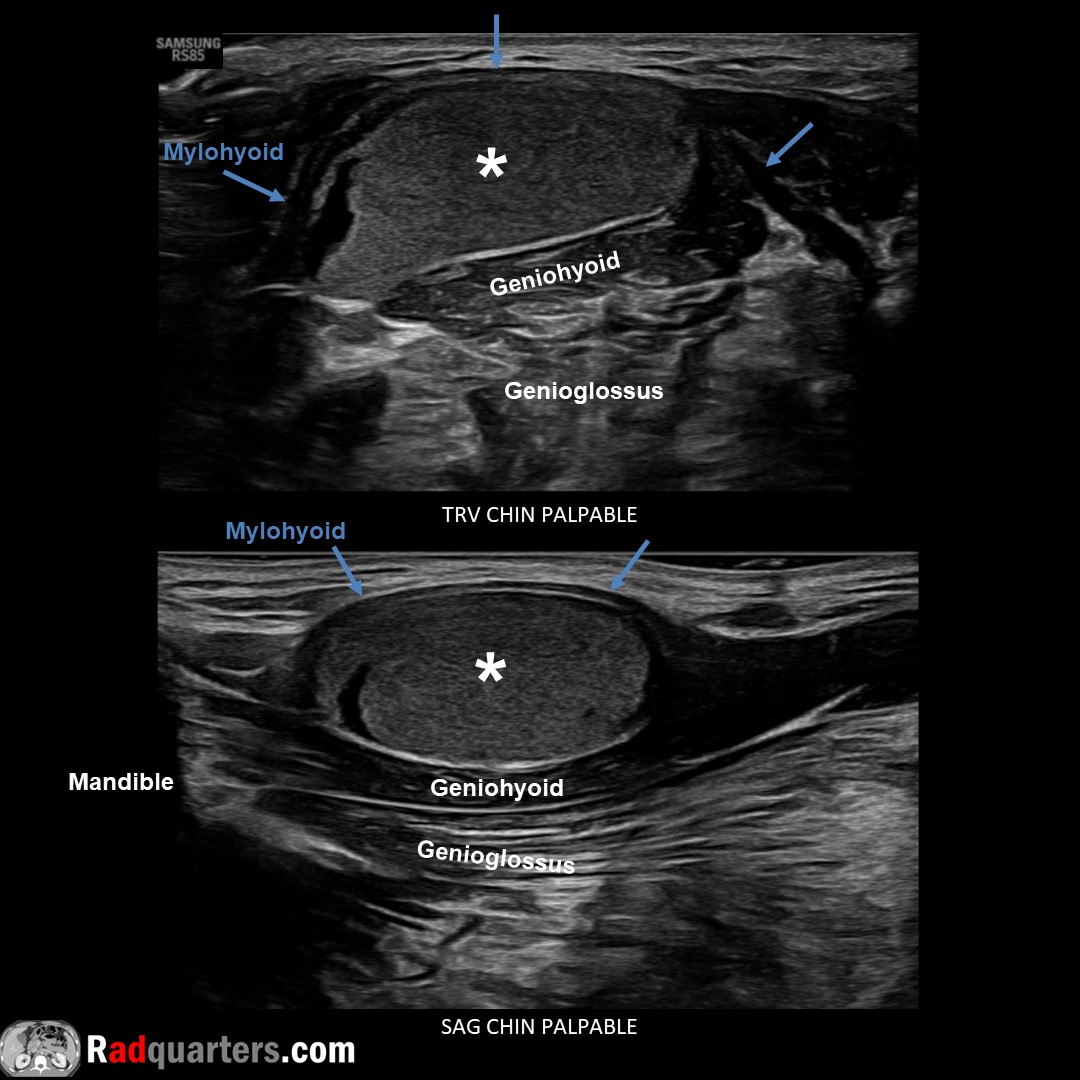
Sublingual dermoid cyst. Rare, benign, squamous epithelial lining & contains skin appendages. Sublingual space bounded medially by genioglossus/geniohyoid muscles, inferolaterally by mylohyoid. Watch📽️ to learn more: bit.ly/subderm
Boston Imaging Samsung Healthcare #FOAMrad

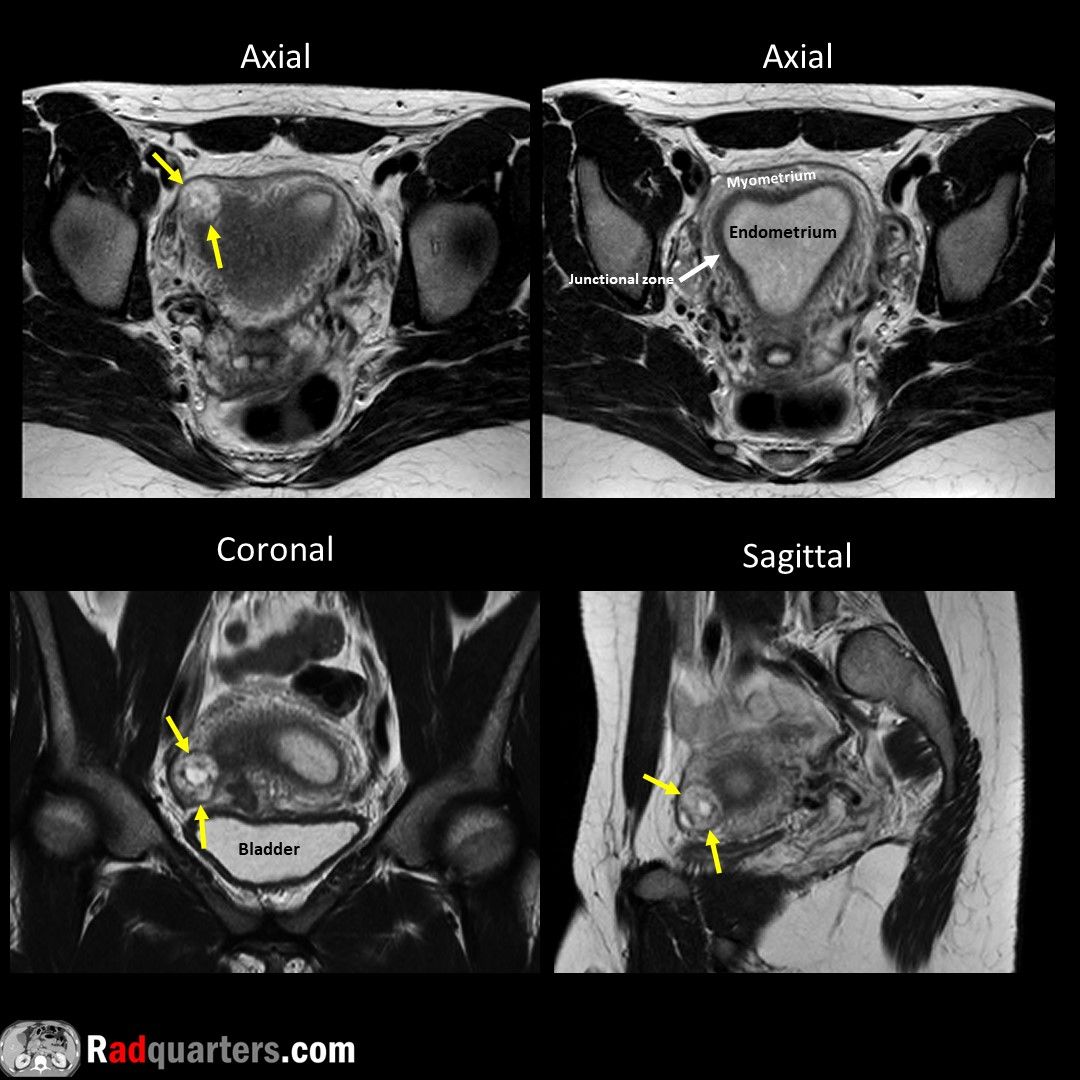
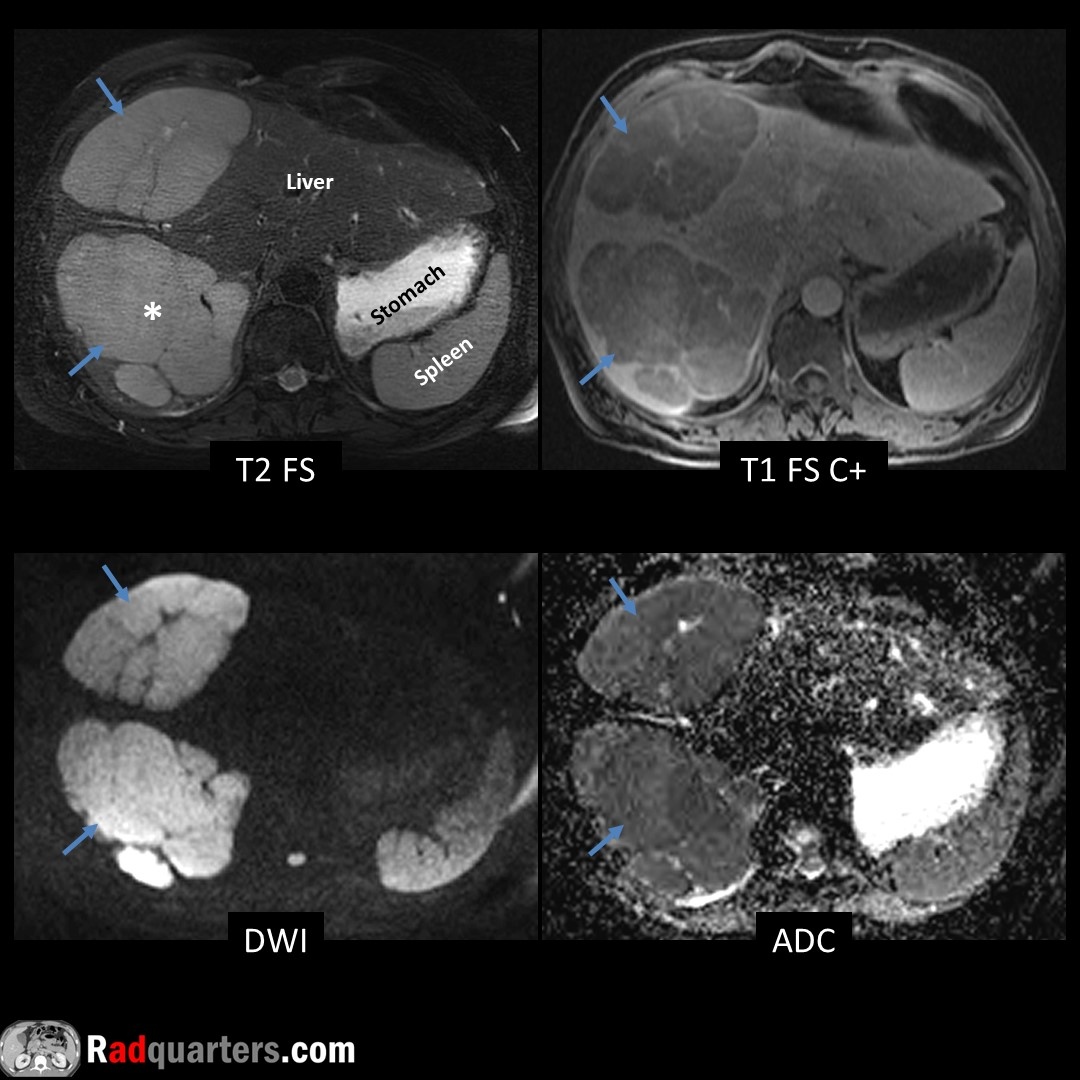
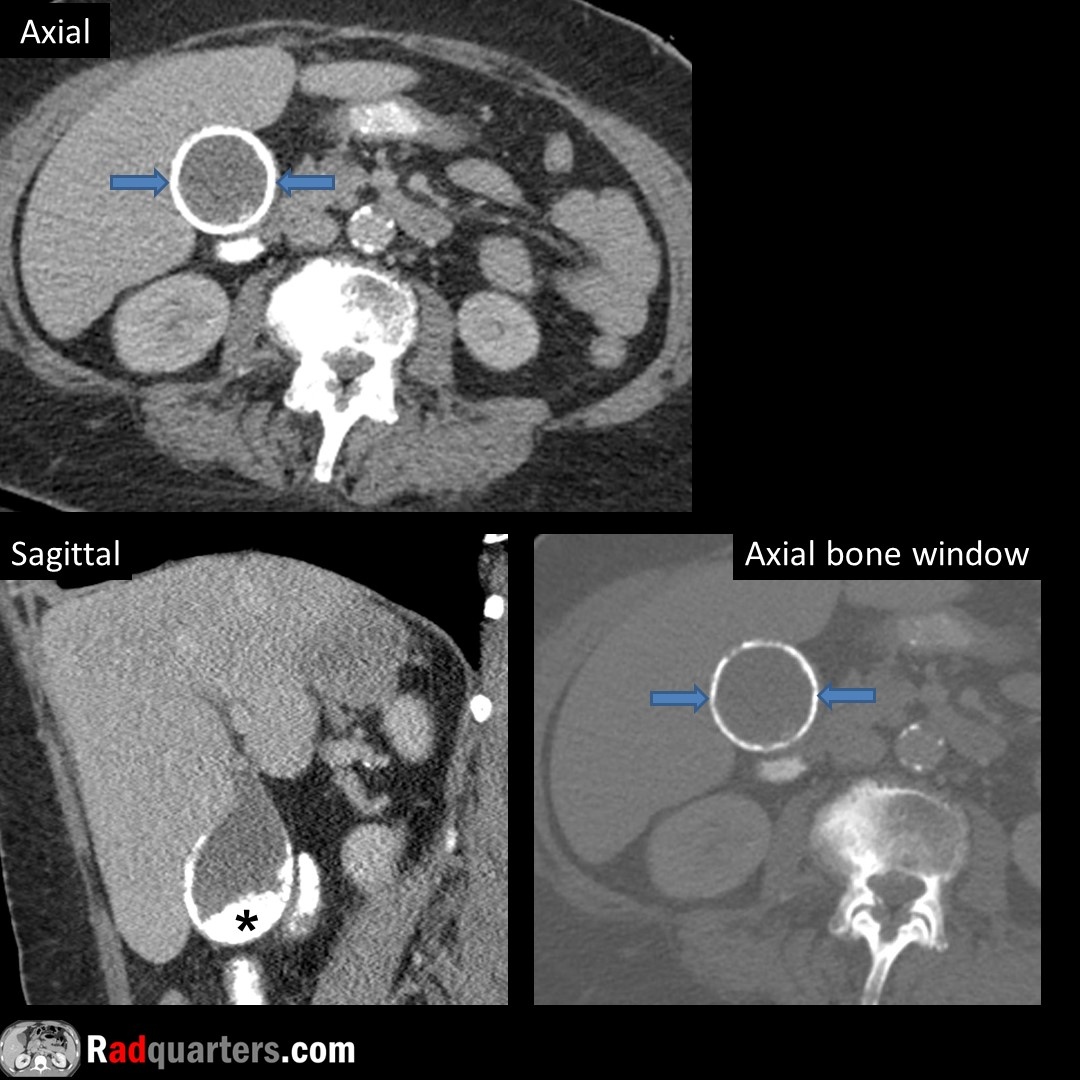
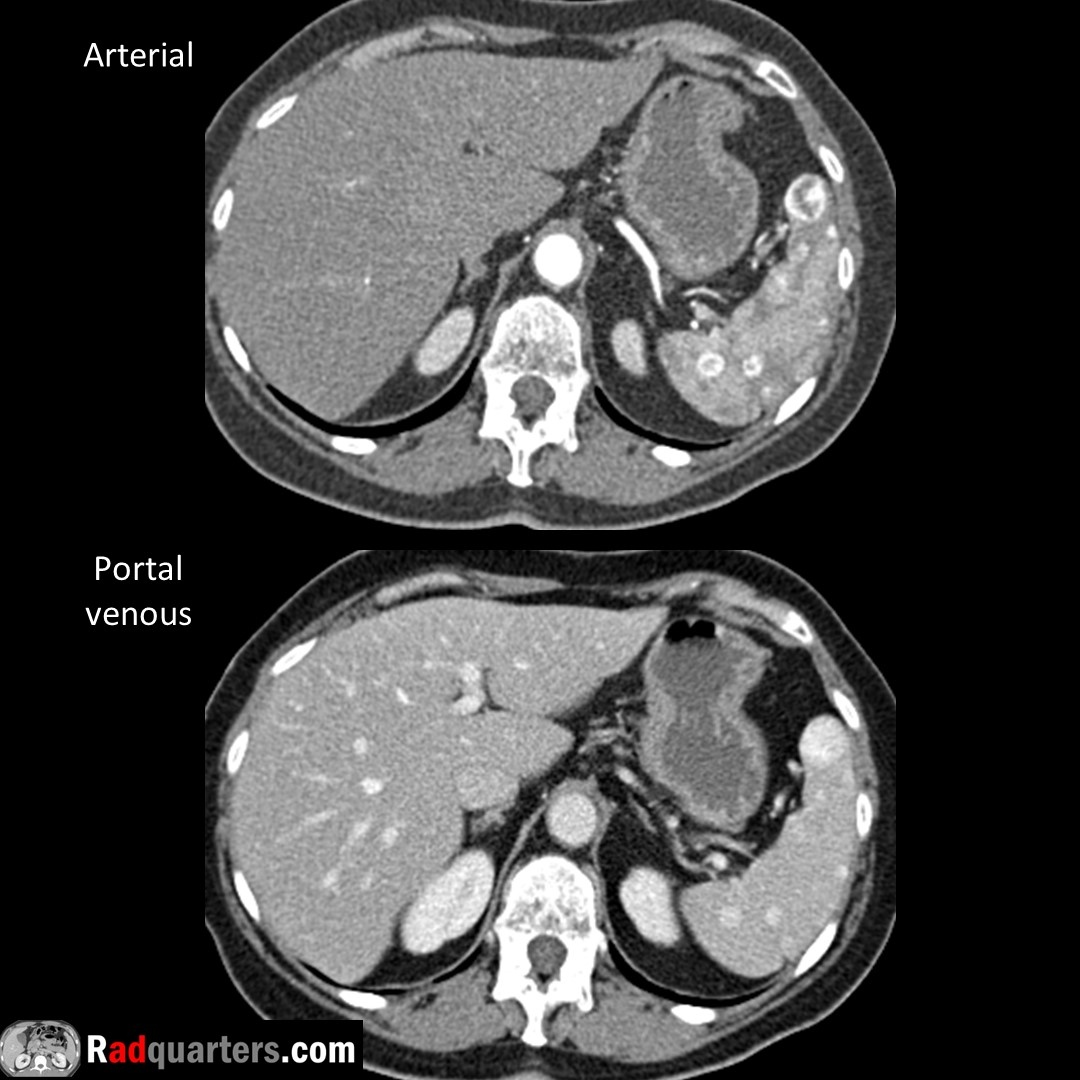
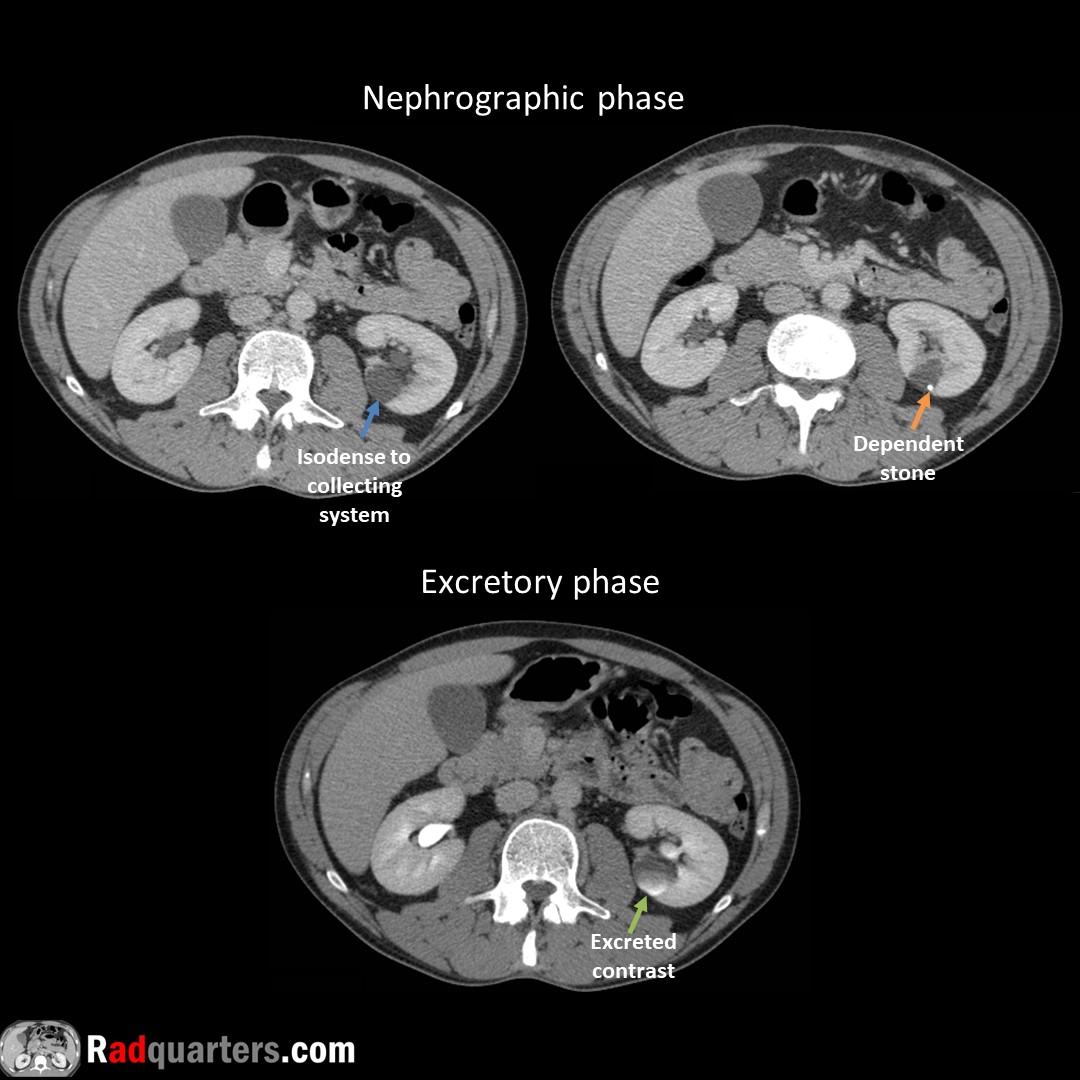
Calyceal diverticulum. Often asymptomatic. Can present with hematuria, stone formation or infection. Mimics cyst on conventional imaging, contains excreted contrast on excretory phase due to communication with collecting system.
#FOAMrad #FOAMed #radres #medstudent #radquarters


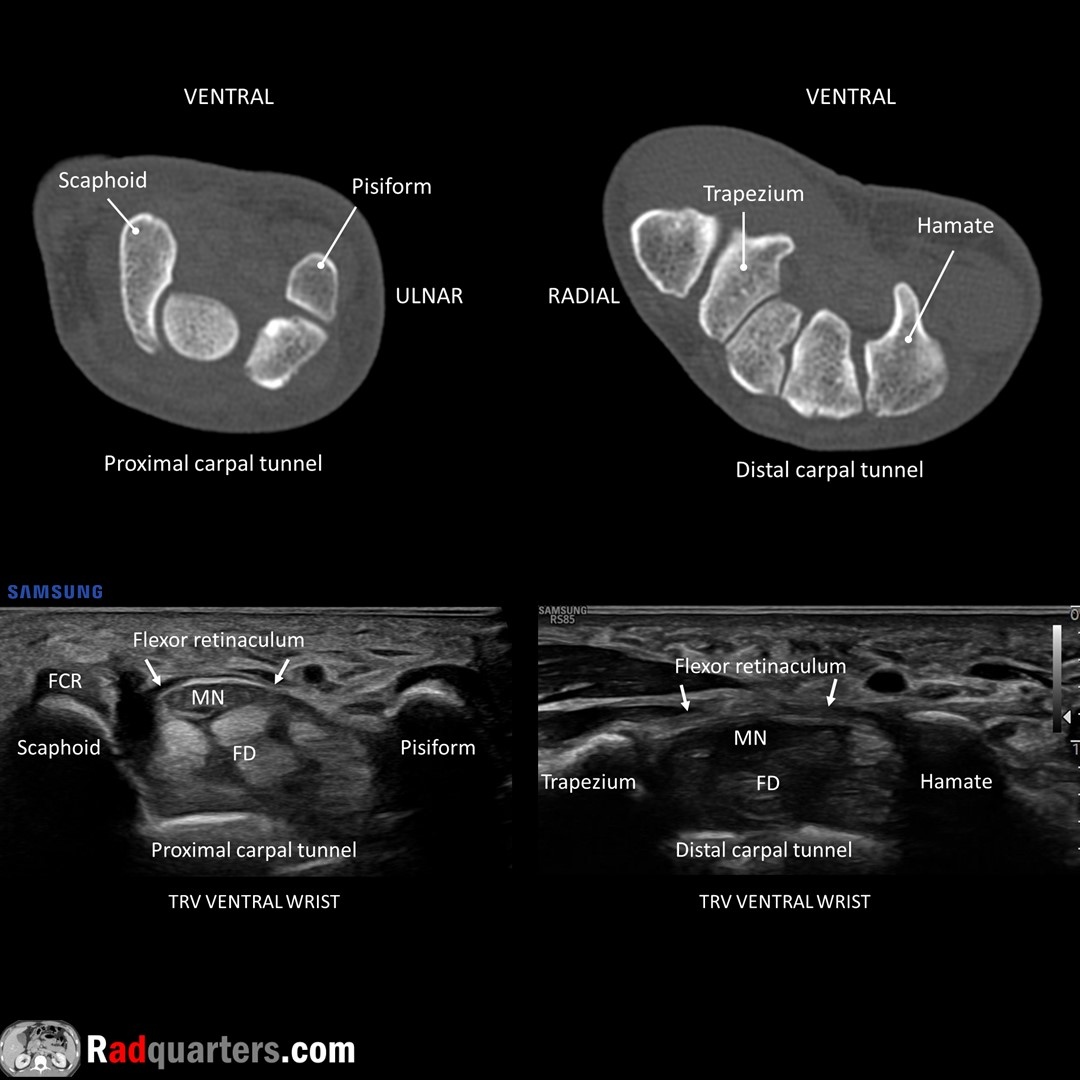
Carpal tunnel anatomy. Median nerve (MN) deep to flexor retinaculum, anterior to flexor digitorum superficialis & profundus tendons (FD). Flexor carpi radialis tendon (FCR) anterior to scaphoid. Watch📽️ to learn more: bit.ly/rq-cts
Boston Imaging Samsung Healthcare #FOAMrad

Join me for “Ultrasound of the Hand & Wrist: What the Surgeon Wants to Know,” a FREE webinar Wed,11/8/2023 at 1 PM EST hosted by the AIUM in conjunction w/ Samsung. Register here: bit.ly/wristwebinar, or go to aium.org. Boston Imaging AIUM Ultrasound #mskrad


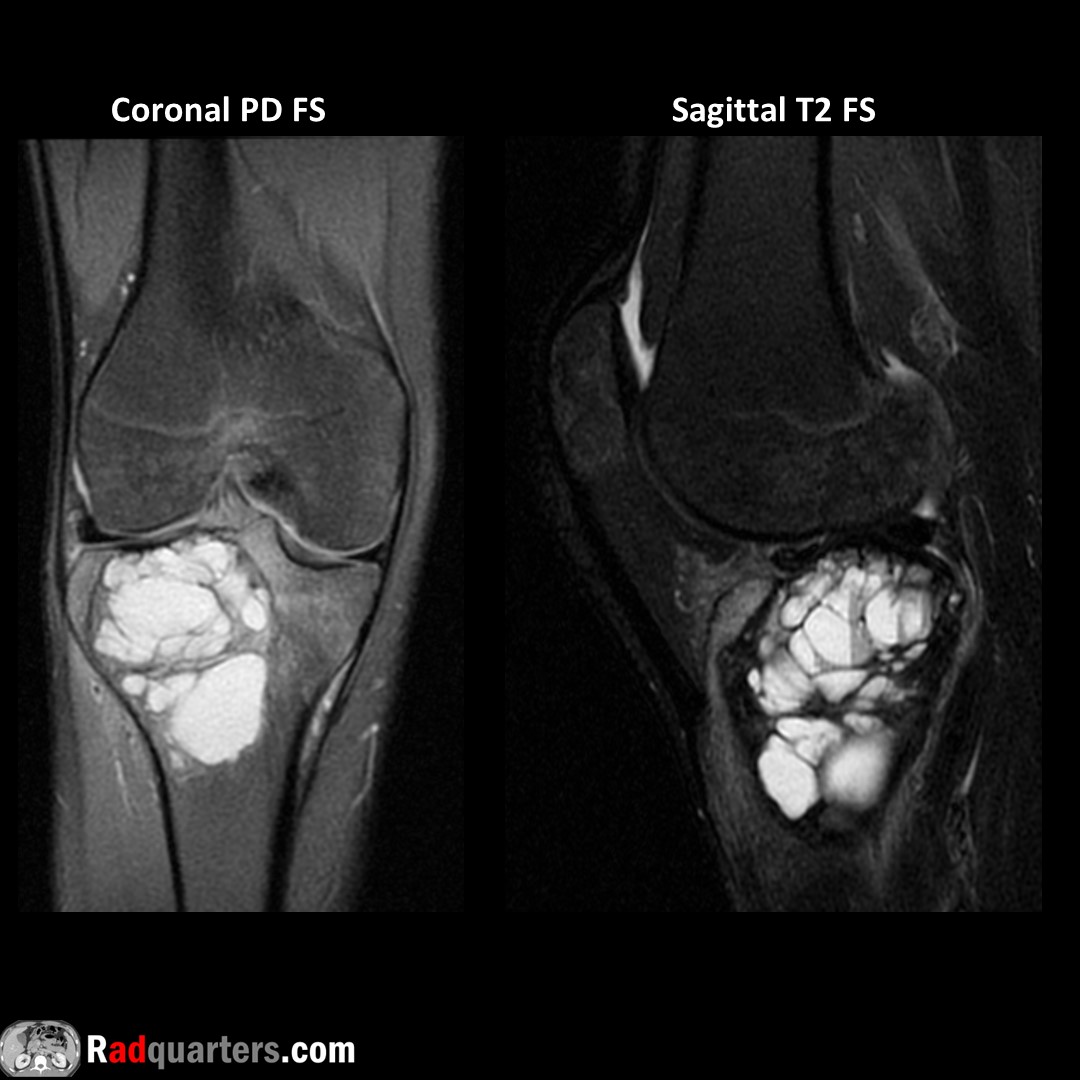
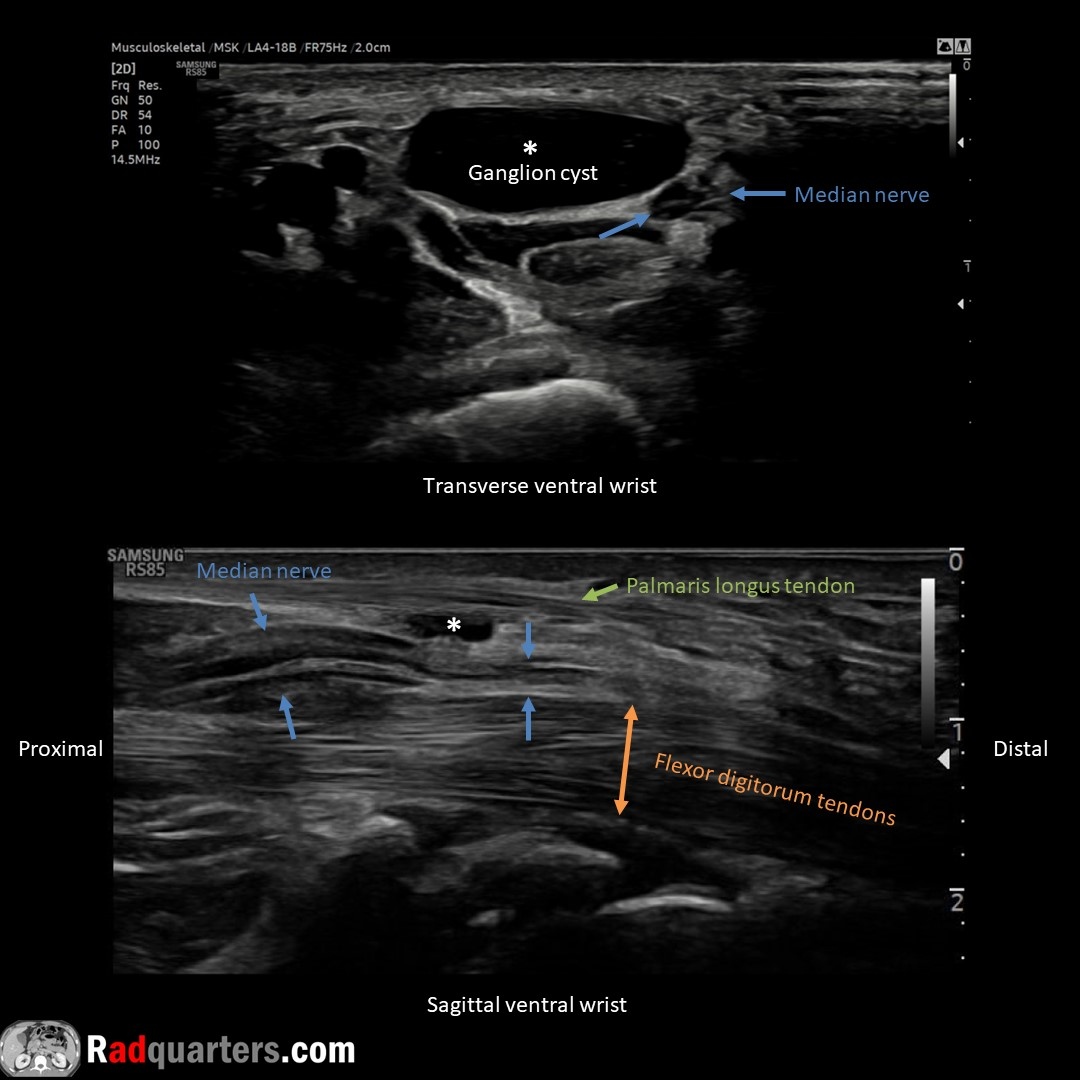
Ventral wrist ganglion cyst causing median nerve compression. MN identified by its fascicular, honeycomb configuration. Thickened nerve proximal to cyst, normal diameter distally = Notch sign. Watch📽️ to learn more: bit.ly/rq-ganglion
Boston Imaging Samsung Healthcare #FOAMrad

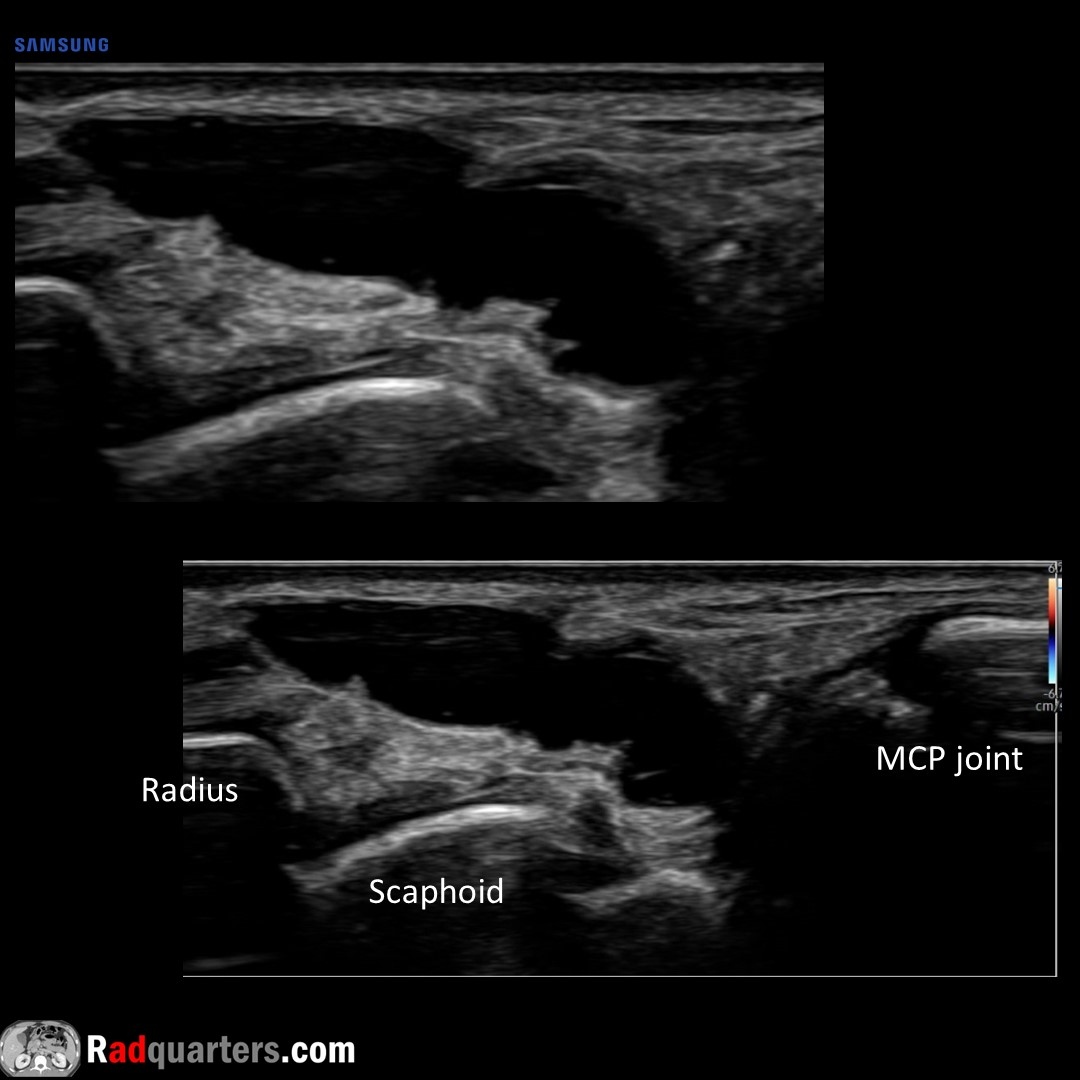
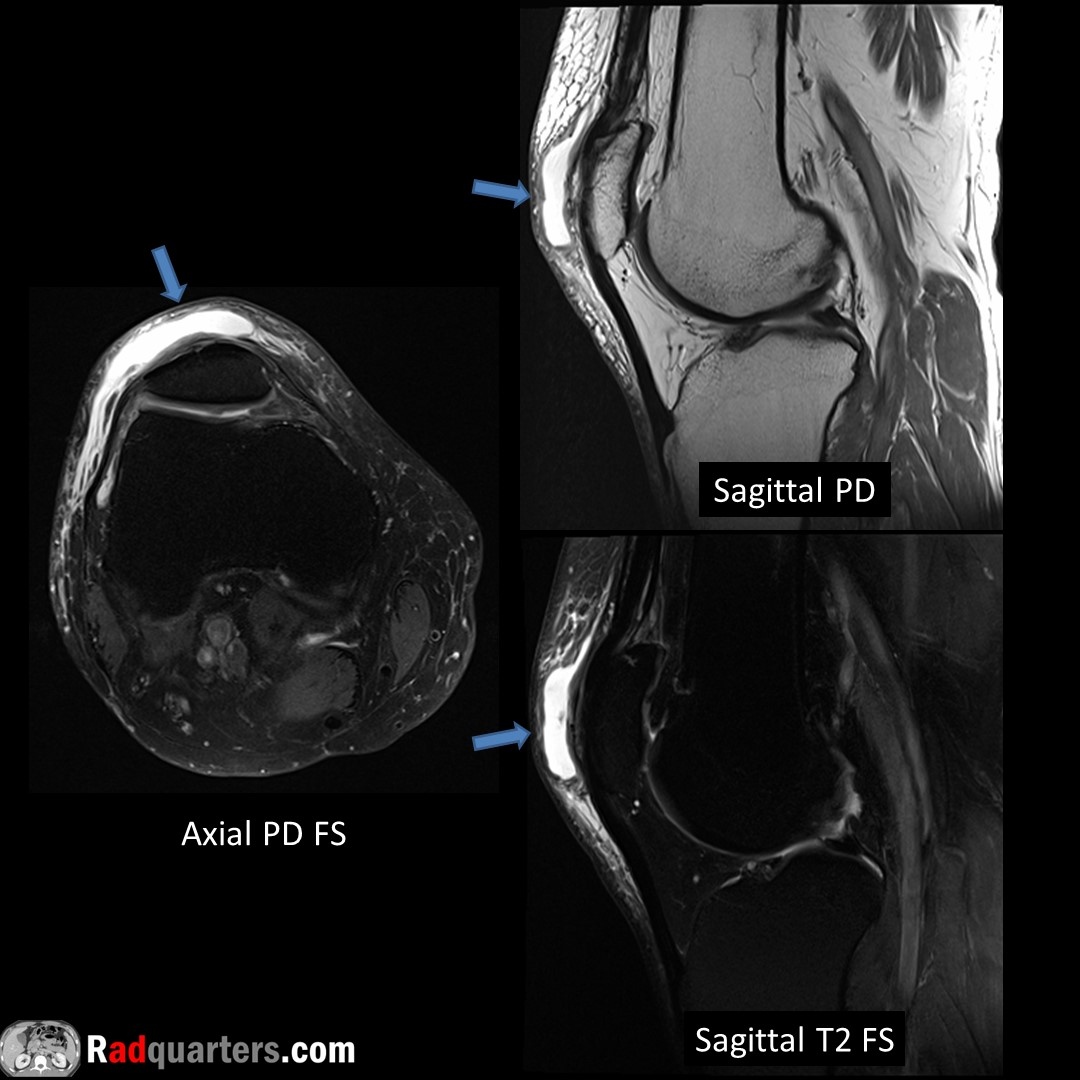
Dorsal wrist ganglion cyst. May see pedicle connecting to joint. Dorsal wrist most common location. Unlike joint recess fluid & bursal collections, will not collapse with compression.
Watch📽️ to learn more: bit.ly/rq-ganglion
Boston Imaging Samsung Healthcare #FOAMrad